Solenoids are like electromagnets. They consist of a large copper - wire coil with a metal slug in the middle. When the coil gets power, the slug is pulled into the coil's center, allowing the solenoid to pull from one end. This particular solenoid is strong and comes with a slanted - cut slug and a great mounting bracket. It acts as an electronic lock for cabinets, safes, or doors. Usually, the lock is engaged, blocking the door from opening as the solenoid slug is in the way, and it consumes no power in this state. When you apply 9 - 12VDC, the slug retracts, letting you open the door. The solenoid comes with a slanted slug. You can open it with two Phillips - head screws and rotate it by 90, 180, or 270 degrees to fit your door. To operate the solenoid, you need a power transistor and a diode. Check the wiring diagram for Arduino or other microcontrollers. A good power supply is required as about 500mA of current rushes into the solenoid to charge the electromagnet. Don't use a 9V battery to power it!
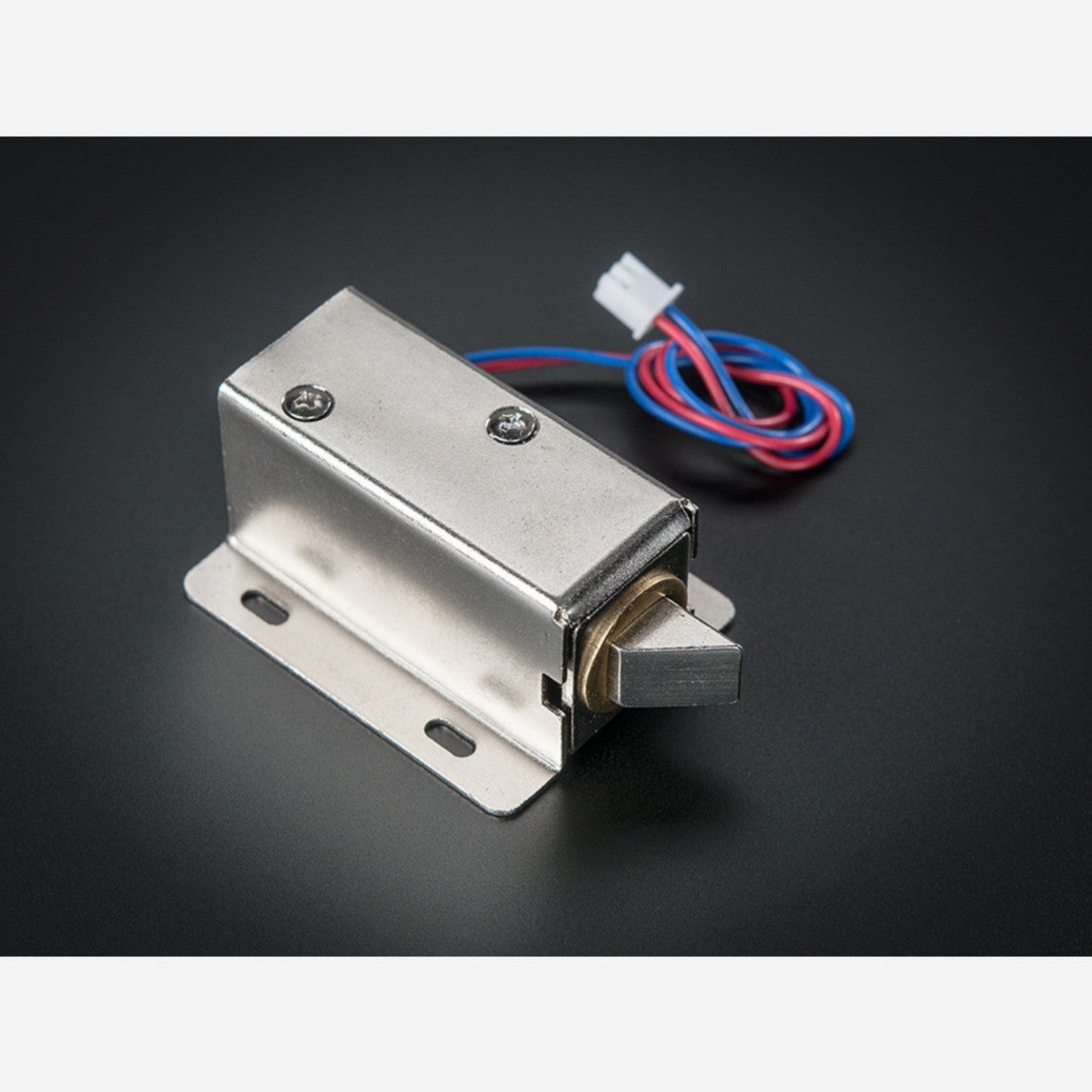
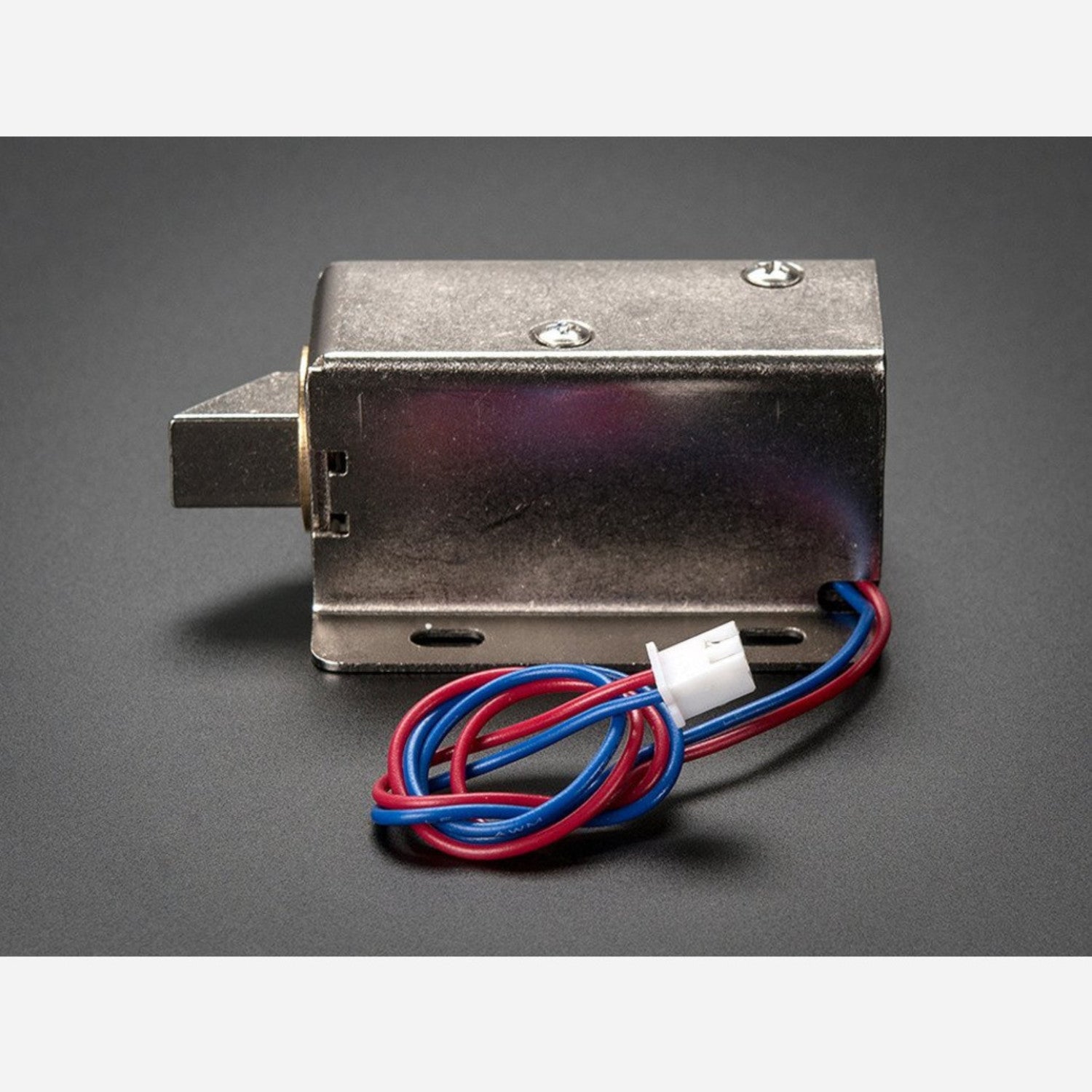

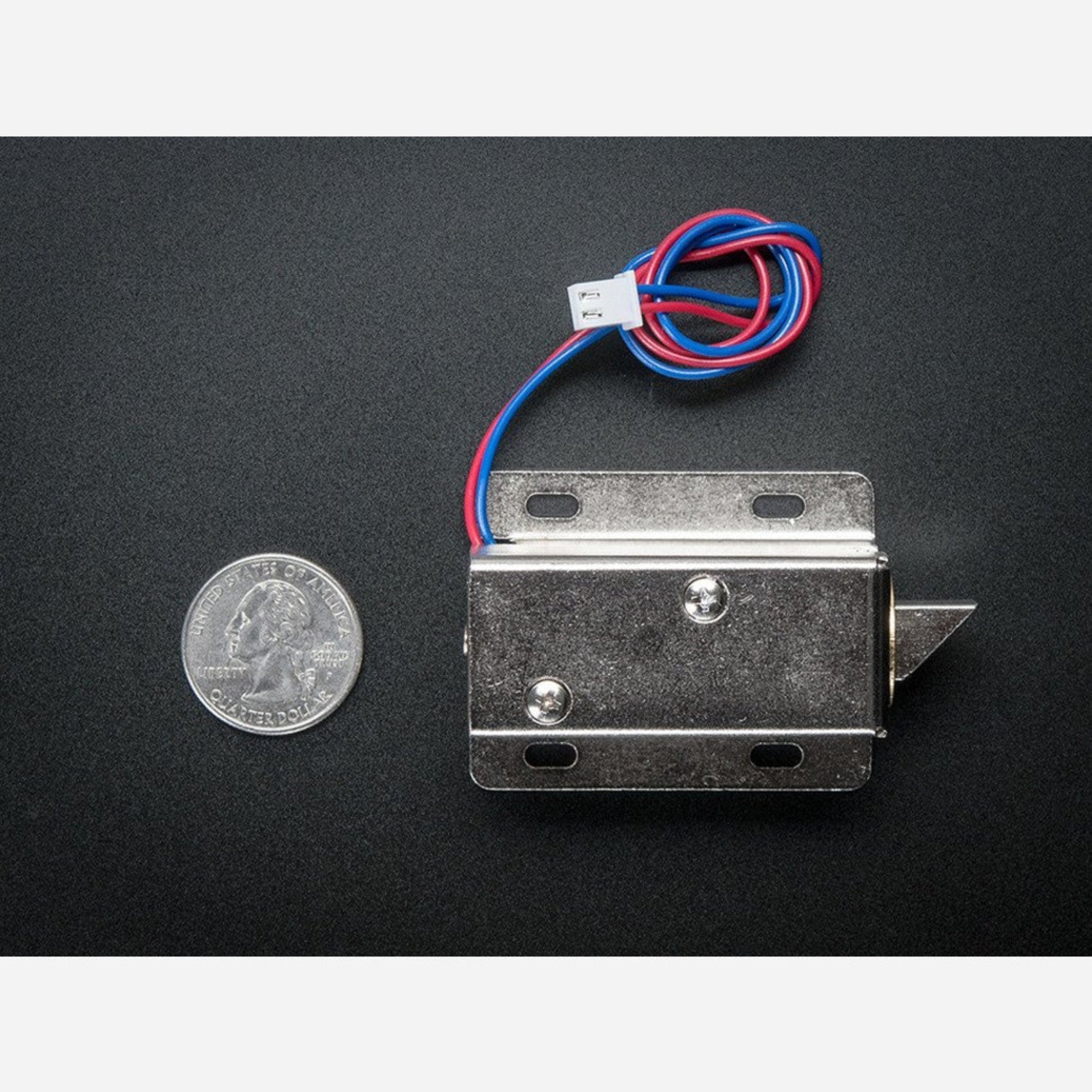


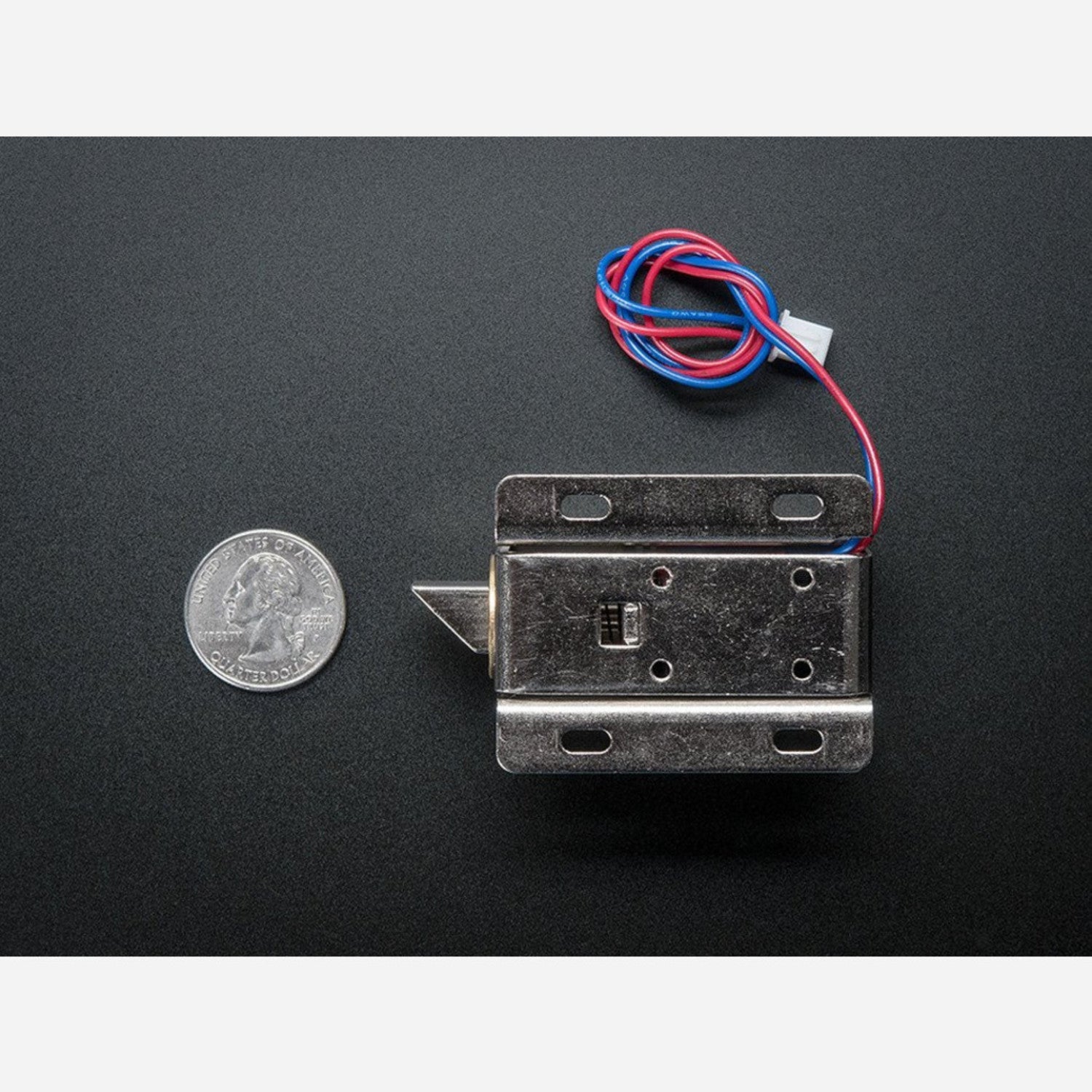
Using this solenoid is quite straightforward. First, make sure you have a suitable power supply. Don't use a 9V battery; a proper power source is needed as the solenoid draws about 500mA of current. Connect the solenoid to a power transistor and a diode as shown in the wiring diagram for your Arduino or microcontroller. When you want to unlock a door, apply 9 - 12VDC to the solenoid. This will retract the slug, and you can open the door. To adjust the position of the slug, use two Phillips - head screws to open the solenoid and rotate the slug by 90, 180, or 270 degrees to match your door. Remember, when the lock is in its normal, locked state, it doesn't use any power. Keep the solenoid clean and free from dust. Avoid over - voltage situations as this can damage the solenoid. If you notice any abnormal behavior, check the wiring and the power supply.







